TYPES OF TRANSPORT IN ROAD TRANSPORT
Trucks, pickup trucks, trailers and containers are used in land transportation. Road transport is the most used mode of transport in passenger transport and freight transport with the advantages it provides. Highways are also preferred for export and import transportation. Road transport has advantages such as ensuring vehicle coordination and fast voyage, ensuring the transfer of goods in the desired amount and weight with the least risk of damage. Trucks, vans, trailers and containers are used in road transport.
TRUCK
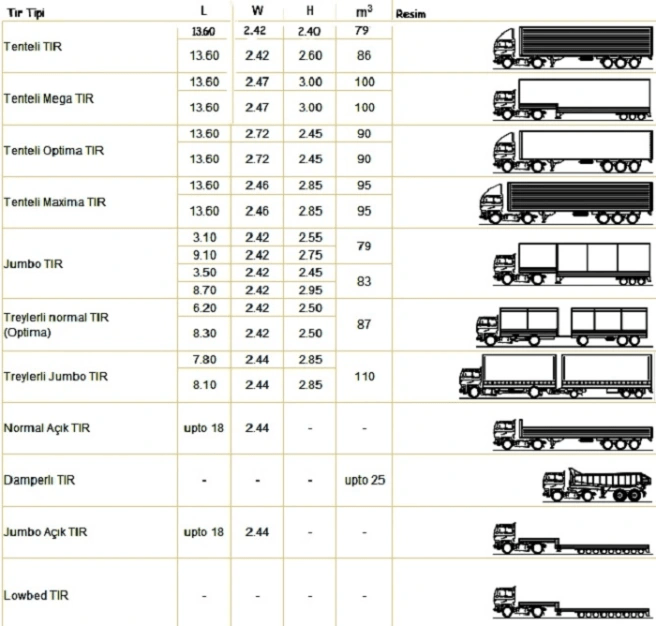
According to the Road Transport Regulation, TIR is a motor vehicle with a maximum loaded weight of more than 3500 kilograms and manufactured to transport goods. The TIR is also called a freight car because it works with the working principle of an automobile. Long trucks that are used in international transportation and carry a blue truck sign are called trucks. The chassis of the TIR is fixed; but the truck can leave the trailer it carries when requested.
The new models of trucks with four axles are known as centipedes in the transport industry. Centipedes, with one tire on their front and middle axles and two tires on their rear axles, with an average load capacity of 20 tons, can reach a total load capacity of approximately 30 tons, including their own weight. These vehicles are frequently preferred due to the fact that they provide great fuel savings compared to old type trucks. Among the most well-known are dump trucks, box trucks, construction trucks, tanker trucks.
Transport vehicles with blue TIR plate, which is an abbreviation formed from the initials of Transports Internationaux Routiers, which means “International Road Transport” in French, are also known as trucks.
TRUCK & VAN
Truck and pickup truck are often confused. While the truck requires a class C driver’s license, the pickup truck is among the vehicles that can be used by those with a class B driver’s license. While trucks are used to transport the heaviest loads, pickup trucks are used to transport furniture, white goods or beverages in the city. The pickup truck differs from trucks in that its maximum permissible laden weight does not exceed 3500 kg. The usage areas of the two vehicles are separated from each other according to their load carrying capacity and speed limits. While both vehicles are used for cargo transportation, the pickup truck can carry a maximum weight of 3.5 tons.
The truck can carry a maximum weight of over 3.5 tons. In a way, pickup trucks are small trucks. Thus, the two vehicles can be seen in different usage areas. Especially pickup trucks are more common in urban transportation. Pickup trucks are preferred because they are more comfortable to use than trucks in traffic. However, trucks are preferred because they can carry more loads in intercity freight transportation. Today, we can see these vehicles more in transportation companies and construction areas. Especially pickup trucks are frequently used to transport goods in the city. These tools are used in many sectors such as white goods and furniture. On the other hand, we see trucks in construction areas. It is often possible to see trucks loaded with giant rocks or construction materials. This type of heavy duty trucks are used. On the other hand, in order to drive a truck in Turkey, you must have a Class C driver’s license. A class B license is sufficient for a pickup truck.
WHAT ARE ROAD TRANSPORT LOADING EQUIPMENT?
PALLET TRUCKS: Pallet trucks, especially used in short-distance freight transportation operations, can work with human power, engine or battery. Two-fork pallet trucks, which are used for handling palletized loads, are generally used in storage areas with a flat floor structure.
RAMPS: Ramps ensure that the transportation vehicles and the loading and unloading area are at the same height, thus enabling the processes to be completed faster. The features and capacities of the ramps can be customized taking into account the characteristics of the facility. In particular, it has a function that facilitates the loading and unloading processes of transport vehicles.
FORKLIFTS: Machines that enable the transport of loads from one point to another via their forks are called forklifts. There are models that are driven by human power, as well as motorized versions. Their capacities can vary from one ton to ninety tons. It is used to put, lift and stack heavy loads on pallets. It provides convenience both in warehouse and in loading.
CRANES: They are used for transporting, loading and unloading large-sized and bulky loads. There are various versions depending on the intended use.
WHAT ARE TRAILER TYPES?
In order to look at the types of trailers, it is necessary to first look at what the trailer is.
WHAT IS TRAILER?
The crates mounted on the back of the vehicles used to carry loads are called trailers. Another name for these vehicle parts is Trailer. This name was established when the trailers produced under the name “Dorsey Trailers” came to our country. Since it is settled in this way in our country, all types of trailers are generally referred to as trailers. Trailers are fixed by mounting to trucks with special mechanisms. There is a special table behind the vehicle for this process. Later, the trailer is connected to the vehicle with apparatus called kingpin.
WHAT ARE TRAILER TYPES?
Trailer types can vary considerably according to their special purposes, coatings and interior features. Carrying capacities are also different from each other. There are types such as Normal Open Trailer, Flat Trailer, Jumbo Trailer.
SLIDING TARPAULIN STANDART TRAILER: 24 TONS GROSS
There are apparatuses that allow the awnings on the sides of the trailer to be opened easily. Thanks to these parts, which are opened by pulling to the sides, such as curtains, it is easier for loading and unloading works.
STOREY SYSTEM TARPAULIN TRAILER: 24 TONS GROSS
It is the situation where there is one or more racking systems in the trailer. Thus, a more systematic and practical work is done in the installation. It is also ideal for dividing your goods into groups.
TRUCK TRAILER TILT TRAILER: 24 TONS GROSS
In this trailer system, in addition to the container the vehicle has, a new trailer is added to the truck like a trailer. This increases the loading volume. At the same time, maneuverability is increased compared to trucks.
CLOSED BODY TERMOKING TRAILER: 21 TONS GROSS
These trailers carry cooling systems inside. In this way, the interior of the trailer can be kept at the desired temperature. It is mostly used for products that are at risk of spoilage such as food, vegetables and fruits, or for materials that need to be transported in the cold, such as pharmaceuticals.
CONTAINER CARRIER TRAILER: 26.5 TONS GROSS
These trailers are designed for container transport only. That’s why even though they appear to consist of only the base, they are well designed for easy mounting and fixing of containers.
AXLE EXTENDABLE SPECIAL TRAILER: 100-140 TONS GROSS
These trailers are used to transport other large vehicles. It is possible to increase its capacity by extending it with additions.
TRAILER AND ITS TYPES
The real meaning of TIR, whose meaning is misunderstood by everyone, is known and used in intercity international freight transportation, as long and wide vehicles transporting on the road. But in fact, TIR is not a vehicle name such as a truck, bus, or train. TIR is an acronym formed from the initials of Transports Internationaux Routiers, which means “International Road Transport” in French. TIR, which started to be used as a common name for all vehicles carrying TIR plates, is now used as the only name for long transport vehicles with trailers. TIR is an agreement signed in Geneva on 15 January 1959 by the International Transport Union (IRU) within the United Nations Organization. In practice, the road vehicles of the countries included in this agreement carry a TIR Carnet indicating the type, quantity and nature of the bonded goods loaded on the vehicle and TIR plates to be affixed to certain parts of the vehicle. The customs control of the goods specified in the TIR Carnet and loaded on the vehicle is carried out in the country of departure, only external controls -except in suspicious cases- are sufficient at the customs of the countries on the route to the destination. In our country, the transportation vehicles consisting of semi-trailer and tow truck are called TIR.
This invention greatly facilitated and accelerated the transportation of commercial goods between countries. The only thing sought is that the trucks and containers that will carry the TIR plate must have protective equipment as specified in the contractual technical specifications. In Turkey, the determination of this issue and the issuance of the Certificate of Conformity, the implementation and control of the TIR contract are carried out by the customs administrations. The Union of Chambers and Commodity Exchanges of Turkey acts internationally as a guarantor institution in terms of compensation against possible losses regarding the taxes of the loads carried by the TIR trucks.
TRAILER
TRAILER
It is a road vehicle with at least one axle, which is pulled by a truck and manufactured according to the characteristics of the load it will carry, and which is connected to the truck to which it is towed with a connection module such as a drawbar, turntable or hook, for the purpose of carrying cargo.
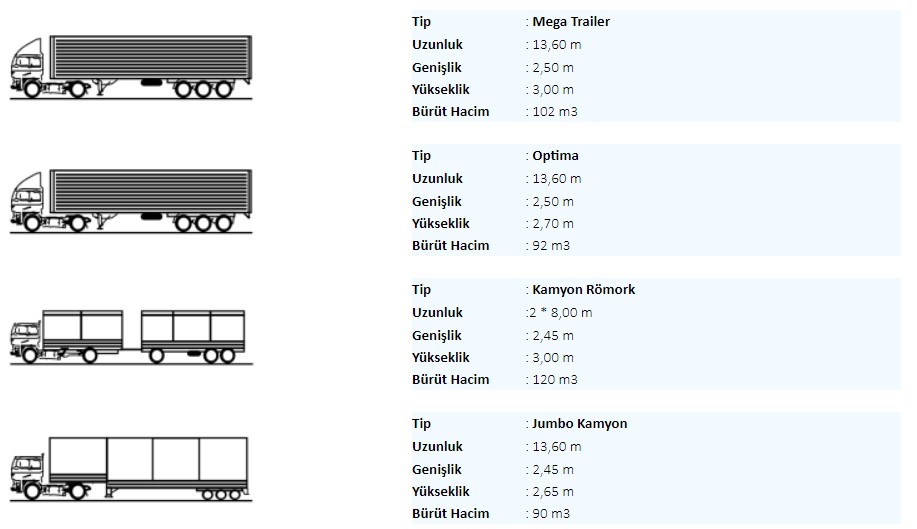
THE MOST USED TRAILER TYPES
- Semi Trailer
- Optima Trailer
- Jumbo Trailer
AWNING TRAILER
Since the awnings surrounding the trailer can be removed one by one, it is possible to load the vehicle from all directions. It is especially suitable for loading and unloading of long products, and it is suitable for all kinds of dry cargo transportation.
THE MOST USED TILT TRAILER TYPES
- Standard Awning trailer
- Trailer with Sliding Curtain Awning
- Roofed Awning Trailer
SEMI TRAILER
It is a road vehicle with at least one axle that is towed by a towing vehicle with an engine and manufactured according to the characteristics of the load it will carry, and which is connected to the vehicle to which it is towed.
THE MOST USED SEMI-TRAILER TYPES
- Tipper chassis semi trailer
- Refrigerated semi trailer
- Maxima semi trailer
TANKERS
Especially used in the transportation of dangerous goods, namely fuel, they are suitable for all kinds of cargo transportation in liquid and gaseous state. It does not have a standard size, it is usually produced according to sectoral expectations and customers’ orders.
CONTAINER CARRIERS
This 20′, 30′, 40′ and long type platform can carry 45′ containers. Axles, the strength of the chassis and locks are very important in container transportation.
THE MOST USED TYPES OF CONTAINER CARRIERS
- Platform type Container carriers
- Long platform type Container carriers
- Fishbone type platform Container carriers
In road transport, cargoes are classified in three different ways:
1) LOADS BY ATTRIBUTES
1A) GENERAL CARGO
A dry and clean shipment that does not require a special service or storage, does not fall into the category of dangerous goods, perishable food or live animals, is called “General Cargo”.
1B) SPECIAL CARGOES
Some cargoes are special in road transportation. Loading, transporting and unloading these products on vehicles requires some additional features compared to other ordinary cargo transportation.
The cargoes that are special in international land transportation of goods are as follows:
- Perishable foodstuffs
- Dangerous materials
- Live animals
2) LOADS ACCORDING TO VEHICLE CAPACITY
If the export or import load fills a complete vehicle, this vehicle is loaded to carry the load of only 1 company. If the amount of load is not enough to fill the vehicle, groupage, that is, partial loading is done. If a partial load is a large-volume load, it is priced according to the space it occupies in the vehicle. If the load is small in volume but heavy, it is priced according to its weight, since the total load carrying capacity of the vehicle is also limited.
- Full truck load (full track loading – FTL)
- Partial (groupage) loads (less than track loading – LTL )
3) LOADS ACCORDING TO DELIVERY PLACE
- Shipments with one loading and one delivery address
- Freights with more than one delivery address
SEA TRANSPORT AND ITS TYPES
Maritime transportation means carrying out the transportation between ports, transporting and sending the products to the desired place, at the desired time, via sea routes. The services to be performed by the expert logistics teams should be shown in terms of delivery time, transactions, international shipments and many more. The products to be sent by sea transport are sent from one point to another with different load options and different systems.
FREIGHT TYPES IN SEA FREIGHT
- Bulk cargo transportation
- General cargo transportation.
- All kinds of transit transportations via Turkey.
- Import and export shipments with containers.
- Industrial goods transport.
- Domestic distribution services.
TYPES OF SEA TRANSPORT
1. TRAMP TRANSPORTATION
In this transportation, it is not possible to deliver the cargo to be transported with the date or time. In addition, goods or cargo belonging to more than one company can be placed on the ship. In addition, the main purpose of tramp transportation is that the ship is full of cargo. It is also known that products such as mines, coal and timber are mostly delivered to their destination by tramp transportation.
2. LINER TRANSPORTATION
In this transportation, the service is more important than the product. When the ship will depart, when it will arrive at the port and which route it will follow is known by the company that owns the cargo. In this tariff-based transportation, mostly Ro – Ro or Container transportation is important.
Sea transport is carried out in many different ways. In particular, the types of transport vary according to the loads. In general, it is essential to state that transportation is divided into five according to goods and cargo;
- Tanker Transportation
- Ro – Ro Transportation
- Container Transportation
- Combined Transport
- Bulk Cargo Transportation
A) TANKER TRANSPORTATION
In general, the transportation of dangerous goods is provided in this way. The transportation of oil, petroleum wastes, all kinds of gas or chemicals is done by tanker transportation. The cargoes are loaded onto the ships mostly by the shore pumping system. Likewise, the transfer takes place in accordance with these criteria.
B) RO-RO TRANSPORTATION
It is one of the cleanest examples of liner transportation in particular. In this transportation model, the sea connection is provided by road. That is, trucks, etc. to ships. Loaded vehicles such as trucks are loaded.
C) CONTAINER TRANSPORTATION
Container transportation is the most common in maritime transportation. With the containers prepared according to international criteria, part loads are transported from one country to another. Containers, which make up 85% of maritime transportation, are also called general cargo transportation.
D) COMBINED TRANSPORTATION
It is a type of transport used mostly for the transport of dry cargo or oil.
E) BULK CARGO TRANSPORTATION
Cement, salt, sugar, etc. It is a type of transportation in which products are loaded and transported.
VEHICLE TYPES
STANDART CONTAINERS (DRYVAN)
Standard containers are containers used for general purposes. These containers are used to transport all kinds of dry cargo. Although the dimensions are usually 20′ and 40′, 45′ and also 54′ length containers have started to be used recently.
HIGH CUBE CONTAINERS
Although this type of container is structurally similar to standard containers, it is a type of container that allows more loading with its 2896mm height than box containers with a height of 2591mm. It is usually produced as 40′. It is used to transport all kinds of dry cargo, light and bulky cargoes and oversized cargoes up to 2.7m in height.
OPEN TOP CONTAINERS
The difference of open top containers from standard containers is that the ceiling part is completely open. After the filling is done, it is closed with a tarpaulin. Generally, its dimensions are 20′ and 40′ in length. Since it allows to put the load from the top, natural usage areas are the cargoes that need to be handled with crane-like equipment with oversized loads that do not fit through the container door.
FLATRACK CONTAINERS
Flatrack containers are transport vehicles consisting of a base platform and two end walls. When necessary, the end walls can be fixed vertically, or they can be closed and laid on the floor to turn into a transport platform. It is generally produced in 20′ and 40′ sizes. Usage areas are heavy tonnage loads, large or high overflow loads. It is also used for the transportation and fixing of high volume break bulk cargoes by creating a platform from two or more flattrack containers.
PLATFORMS (PLATS)
Platforms are structurally only in the form of a base platform. It has no end and side walls. It is suitable for carrying heavy tonnage loads in small area. Sizes are generally produced as 20′ and 40′. Usage areas are oversize loads and heavy tonnage loads.
VENTILATED CONTAINERS
Ventilated containers are the type of containers that allow natural air circulation through the ventilation channels in the top and bottom profiles. Generally, it is produced as 20′ in size. Its usage areas are loads that must be carried in an airy environment. It is widely used for transporting green coffee grains.
REEFER CONTAINERS
Reefer containers are specially insulated containers with a cooling unit inside. It is generally produced in 20′ and 40′ sizes. High cube containers are used to transport light and bulky loads (flowers, fruits, etc.). They are food products that are transported at constant temperature, whose natural use is below or above 0 ºC.
BULK CONTAINERS
Bulk cargo containers are containers with 3 loading doors on the ceiling and 2 discharge doors on the door. Generally, it is produced as 20′ in size. Usage area: animal feed, grain, spice etc. the transport of loads.
TANK CONTAINERS
These are the containers that consist of a tank with a carrier feature and a profile frame surrounding it.
CONTAINER TYPES
20′ STANDARD DRY VAN (DC)


40′ STANDARD DRY VAN (DC)


40′ HIGH CUBE DRY (HC)

This type of container is used to transport relatively light but high volume goods. Their height is 30 cm higher than a normal 40′ container.

20′ OPEN TOP (OT)


40′ OPEN TOP (OT)


40′ OPEN TOP HIGH CUBE (OTHC)


GENERAL INFORMATION FOR OT CONTAINER (20-40-DC/HC—OT)
*** It carries the length and width dimensions of a typical general purpose container, with the only difference being that it does not have a “fixed top”. It is used in cases where loads that are too long/wide to fit into the container through the door can only be loaded from the top with cranes or similar vehicles. Mostly machinery, marble plates, aluminum profiles etc. are transported. Open top containers are often used for overflowing loads. It is tightly covered with a tarpaulin after loading. Its base is slightly thicker because it carries heavy loads, and a surcharge is usually added to the freight since it falls under the special equipment class.
40′ PALLET WIDE – SEA CELL (PWSC)

40′ PALLET WIDE – SEA CELL HIGH CUBE (PWSC-HQ)

GENERAL INFORMATION FOR PALLET WIDE CONTAINER
It is also sometimes referred to as “flat” for short. This type of container does not have two sides and a top. Sometimes both heads can be dislodged. A lot of surcharge may be added to the freight because the flat container is suitable for loading goods from both sides and overflowing. The bottom of the container is very thick.
20′ FLAT RACK (FR)


40′ FLAT RACK (FR)


40′ REEFER HIGH CUBE (RFHQ)


GENERAL INFORMATION FOR REFRIGERATED CONTAINERS
It is used for the transportation of other cargoes, especially food products, with cooling control, with a cooling unit installed in the container and operated by an electric or diesel engine.
SHIP TYPES
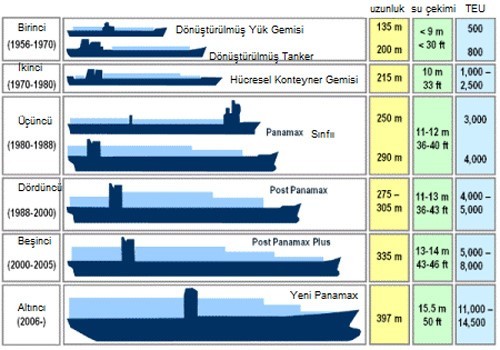
1) HANDYSIZE
Handysize vessels have a maximum carrying capacity of 39,999 dwt. These vessels are mainly engaged in transporting small bulk cargoes. These vessels are increasingly operating within the scope of regional trade routes. Handysize vessels are ideal for small ports with length and draft restrictions. The ship’s cargo equipment allows them to serve in the vessels where there is a lack of infrastructure for loading and unloading cargo. Handysize vessels are mainly built at shipyards in Japan, South Korea, China, Vietnam, India and the Philippines. A number of other countries also have the expertise and capacity to build small bulk carriers. The most common handysize vessels built today are 32,000 DWT with 10 m (33 ft) draft. These ships have four overhead cranes and five cargo holds for cargo handling. Some non-handy ships are also equipped with stanchions for easy loading of wooden logs on the deck. Handysize vessels have a maximum carrying capacity of 39,999 dwt. These vessels are mainly engaged in transporting small bulk cargoes. These vessels are increasingly operating within the scope of regional trade routes. Handysize vessels are ideal for small ports with length and draft restrictions. The ship’s cargo equipment allows them to serve in the vessels where there is a lack of infrastructure for loading and unloading cargo. Handysize vessels are mainly built at shipyards in Japan, South Korea, China, Vietnam, India and the Philippines. A number of other countries also have the expertise and capacity to build small bulk carriers. The most common handysize vessels built today are 32,000 DWT with 10 m (33 ft) draft. These ships have four overhead cranes and five cargo holds for cargo handling. Some non-handy ships are also equipped with stanchions for easy loading of wooden logs on the deck.
2) HANDYMAX/SUPRAMAX
Handymax and Supramax are bulk carriers with a capacity of less than 60,000 dwt. The capacity of a Handymax vessel is usually between 35,000 and 50,000 DWT, while Supramax vessels are slightly larger, with 50,000 to 60,000 DWTs. Modern handymax designs are usually 52,000-58,000 DWT in size. These bulk carriers are ideal for small ports with length and draft restrictions, or ports that do not have a freight transfer infrastructure. As a result, Handymax and Supramax bulk carriers represent the majority of bulk carriers over 10,000 DWT. Although these bulk carriers are mainly used to transport dry cargo such as iron ore, coal, cement, finished steel, fertilizer and grain, this category is also occasionally used to describe small-sized oil tankers.
Alongside the Handysize vessels, the Handymax and Supramax vessels are considered among the smallest bulk carriers in operation today. A handymax vessel is typically 150-200 m (490-655ft) long with 5 cargo holds and 4 cranes with a lifting capacity of 30 metric tons. As these ships are equipped with on-deck cranes, they offer the best option for hauling cargo to less developed ports. These bulk carriers are used for small-volume dry cargo transportation and even allow the transportation of different types of cargo in different warehouses. Supramax vessels in the Handymax category are in high demand from shippers due to the greater cargo carrying capacity of Panamax vessels and the flexibility of cargo handling on board. The appropriate size of these vessels allows trading in more ports and terminals worldwide. It is estimated that the Supramax category accounts for over 90% of the handymax ships built today. Handymax ships are built mainly in Asian shipyards, primarily in Japan, South Korea and China.
3) PANAMAX
The carrying capacity of Panamax ships is in the range of 60,000-79,999 dwt. These ships carry small bulk cargoes such as coal, iron ore, grains and, to a lesser extent, steel products, cement and fertilizers. Panamax vessels can pass through the Panama Canal, making them more versatile in terms of accessing different trade routes. Most Panamax and Post-Panamax vessels are unequipped and therefore shore-based cargo handling equipment must serve these vessels. However, there are also a small number of ships equipped with onboard cranes, which increase trade flexibility and allow operation in ports with insufficient infrastructure in terms of loading and unloading possibilities. Panamax vessels can pass through the Panama Canal, making them more versatile in terms of accessing different trade routes. Most Panamax and Post-Panamax vessels are unequipped and therefore shore-based cargo handling equipment must serve these vessels. However, there are also a small number of ships equipped with onboard cranes, which increase trade flexibility and allow operation in ports with insufficient infrastructure in terms of loading and unloading possibilities.
4) POST-PANAMAX
The carrying capacity of Post-Panamax ships is in the range of 80,000 – 109,999 dwt. These vessels tend to have shallower draft and width with higher payload compared to standard Panamax vessels. Although they cannot transit through the Panama Canal, these vessels are specifically designed to load high cubic loads from ports with restricted draft.
5) CAPESIZE
The carrying capacity of Capesize ships is in the range of 110,000-199,000 dwt. Only the longest ports in the world have the infrastructure to accommodate ships of this size. Capesize vessels are mainly used to transport iron ore or coal and, to a lesser extent, grain, often on long-distance routes. The Capesize category consists of large bulk carriers and tankers generally above 150,000 deadweight tonnage (DWT). They are much larger in both draft size and DWT compared to Panamax and Suezmax vessels and are therefore categorized under VLCC, ULCC and bulk carriers. Capesize vessels with a DWT of up to 400,000 DWT are currently being built to meet the demand for very large bulk carriers.
Capesize ships are too large in size (especially drafts) to pass through the Panama Canal. Therefore, in order to navigate between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, they must transit through Cape Horn. In the past, these ships, which were not suitable for passing through the Suez Canal, had to circumnavigate a long route via the Cape of Good Hope in order to navigate between the Indian Ocean and the Atlantic Ocean. However, the Suez Canal was deepened from 18 meters (60 ft) to 20 meters (66 ft) in 2009, allowing many capesize vessels to pass through the canal. Due to their large size and deep draft, these capesize vessels are only suitable for serving major ports in the world with deep water terminals. As a result, these vessels are able to serve a relatively small number of ports worldwide. These ships are generally used to transport coal, iron ore and raw materials. For this reason, they are often referred to as bulk carriers rather than tankers.
6) LARGE IRON ORE VESSELS (VLOC)
The subcategory of Capesize vessels includes large iron ore vessels (VLOC) above 200,000 DWT and large bulk carriers (VLBC). These ships are mainly designed to transport iron ore. According to estimates, 93% of the cargo of capesize bulk carriers consists of iron ore and coal. While a standard capesize vessel is around 175,000 DWT, bulk carriers of 400,000 DWT or more have recently been built to meet the ever-increasing demands of bulk ore shipping companies. There is a great demand for large capesize vessels in the world today. The order book for capesize bulk carriers greater than 200,000 DWT has been on the rise in recent years. But only a few of the world’s ports have the infrastructure to handle vessels larger than 200,000 DWT, port access has emerged as a major challenge for capesize vessels. Today, the majority of large capesize bulk carriers are used to transport ore between Australia-China and Brazil-China.
CONTAINER SHIPS
AIRWAYS TRANSPORTING

Today, the airline industry receives much more attention than other types of transportation, and this interest is increasing day by day. The industry has remained in a constant process of change since the very first years of air transportation. The increasing bloc between countries after the Second World War and the cold war made the already existing socioeconomic differences more evident. Great economic and political differences between countries and the relations between these countries have affected the airline sector as well as the sectors all over the world. One of the characteristics of the airline industry is that it is extremely sensitive to national and international policies. On the other hand, countries always want to keep the airline industry under their own control. For this reason, international air transport has been shaped within the framework of the countries’ own policies. One of the most important effects and indicators of this is that the airline companies have determined on which routes they will operate with the bilateral agreements made by the countries. In this case, the market access and access opportunities of the airline companies are determined not in line with their own goals, targets and strategies, but in line with the policies determined by the countries by considering various factors.
CARGO TRANSPORT UNITS
Airline cargo transport units play a facilitating role in the collection and collection of part loads and their transportation under appropriate conditions, that is, in providing standard and safe service. Essentially, the purpose of cargo transport systems is to separate the cargo into units and, after completing this process, transport it from one point to another destination in container-like units. The loading capacities of aircraft vary according to aircraft types and the dimensions of the aircraft’s cargo door. Air cargo is usually transported in airline containers and pallets. These speed up and facilitate the transfer of goods at the airport during loading and unloading. When calculating cargo costs, the weight of the cargo and the volume it occupies are also taken into account. If the packaging of a light cargo is large, the cost will be high. LEARNING ACTIVITY–3 OBJECTIVE RESEARCH 22-49 There are limitations regarding the weight of the loads that aircraft can carry in air cargo transportation. In this regard, cargo should be transported by dividing it into the smallest possible amount in terms of weight.
PALLETS USED IN AIRLINE CARGO TRANSPORT
The five most commonly used standard-sized basic pallets are as follows. These dimensions are: 1334 x 3175 mm. (60.4 x 125 inches) 2235 x 2743 mm. (88 x 108 inches) It is a standard pallet used in the transport of livestock and dangerous goods. 2235 x 3175mm. (88 x 125 inches) 2438 x 3175 mm. (96 x 125 inches) 2438 x 6057 mm. (96 x 238.5 inches) Tracks of this size are usually 1 inch thick and have “seat tracks” on the sides. Sometimes instead of these, there are mesh joining points on the edges of the pallets. Pallets also form the lower parts of some other units.
1) MAIN (UPPER) WAREHOUSE NETWORK PALLET – IATA 1/1S TYPE (MAIN DECK PALLET WITH NET – IATA TYPE 1/1S-IATA PREFIX: PG)
MAXIMUM LOAD CAPACITY: Dimensions (width x length x height): 13,680 kg. / 30,000 lb. 6,058mm. x 2,438mm. x 2,438mm. 1 lb. = 0.455 g. (238.5 inches x 96 inches x 96 inches) (1 inch = 2.54 cm)
VOLUME & AVAILABLE AIRCRAFT TYPES: 33.25 m3 / 1,174 ft3 Boeing 747F ft3 :(cubic foot), (cubic foot) = 28.32 liters
TARE: 400 kg. / 882 lb.
2) MAIN DECK PALLET WITH NET – IATA TYPE 2/2Q-IATA PREFIX: PM
MAXIMUM LOAD CAPACITY: Dimensions (width x length x height): 6,804 kg. / 15,000 lb. 3,175mm. x 2,438mm. x 2,438mm. 1 lb. = 0.455 g. (125 inches x 96 inches x 96 inches) (1 inch = 2.54 cm)
VOLUME & AVAILABLE AIRCRAFT TYPES: 17.16 m3 / 606 ft3 DC 10-30 cargo plane, Boeing 747F
TARE: 130 kg. / 287 lb.
3) MAIN WAREHOUSE NETWORK PALLET – IATA 2H TYPE
MAXIMUM LOAD CAPACITY: Dimensions (width x length x height): 6,804 kg. / 15,000 lb. 3,175mm. x 2,438mm. x 2,997mm. 1 lb. = 0.455 g. (125 inches x 96 inches x 118 inches) (1 inch = 2.54 cm)
VOLUME & AVAILABLE AIRCRAFT TYPES: 21.16 m3 / 747 ft3 DC 10-30 cargo plane, Boeing 747F
TARE: 130 kg. / 287 lb.
4) NETWORKED PALLET – IATA 2WA TYPE (PALLET WITH NET – IATA TYPE 2WA – IATA PREFIX: PM)
MAXIMUM LOAD CAPACITY: Dimensions (width x length x height): 4,626 kg. / 12,200 lb. 3,175mm. x 2,235mm. x 1,626mm. 1 lb. = 0.455 g. (125 inches x 88 inches x 64 inches) (1 inch = 2.54 cm)
VOLUME & AVAILABLE AIRCRAFT TYPES: 9.91 m3 / 350 ft3 DC 10-30, Boeing 747, 747F, 777, 767-300
TARE: 120 kg. / 264 lb.
5) NETWORKED PALLET – IATA 5 TYPE (PALLET WITH NET – IATA TYPE 5 – IATA PREFIX: PA)
MAXIMUM LOAD CAPACITY: Dimensions (width x length x height): 5,035 kg. / 11,100 lb. 3,175mm. x 2,438mm. x 1,626mm. 1 lb. = 0.455 g. (125 inches x 96 inches x 64 inches) (1 inch = 2.54 cm)
VOLUME & AVAILABLE AIRCRAFT TYPES: 15.8 m3 / 557 ft3 DC 10-30, Boeing 747, 747F
TARE: 130 kg. / 287 lb.
6) BOTTOM WAREHOUSE NETWORK PALLET – IATA 6 TYPE
MAXIMUM LOAD CAPACITY: Dimensions (width x length x height): 3,175 kg. / 7,000 lb. 3,175mm. x 1,534mm. x 1,626mm. 1 lb. = 0.455 g. (125 inches x 60.4 inches x 64 inches) (1 inch = 2.54 cm)
VOLUME & AVAILABLE AIRCRAFT TYPES: 6.94 m3 / 245 ft3 Airbus 300, Boeing 747, 747F,
TARE: 90 kg. / 198 lb.

You can also follow our Instagram Account!